Lumbar osteochondrosis is a pathological change of the cartilage and bone tissue of the lumbosacral disc. This change may be natural or the result of an unhealthy lifestyle. In old age, the degeneration process of bone and cartilage tissue of all people begins. But when these phenomena are immature (appearing in middle-aged people), then we are talking about the pathological process of the skeletal system. Pathology also affects men and women over 30 years of age.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is the most famous and common disease in the spine, manifested by severe pain in the waist. The disease is the result of insufficient nutrition of cartilage and bone tissue due to metabolic disorders, and the accumulation of waste products in bone cells. This can lead to disease of the intervertebral disc. In addition, their thickness and flexibility change, and then grow in the form of osteophytes (growth of bone tissue that causes narrowing of the nerve ending holes) on the vertebrae.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
Lumbar osteochondrosis is more common than thoracic or cervical osteochondrosis, because the lower back bears the greatest load when walking and running, sitting in a chair for long periods of time, or lifting weights.
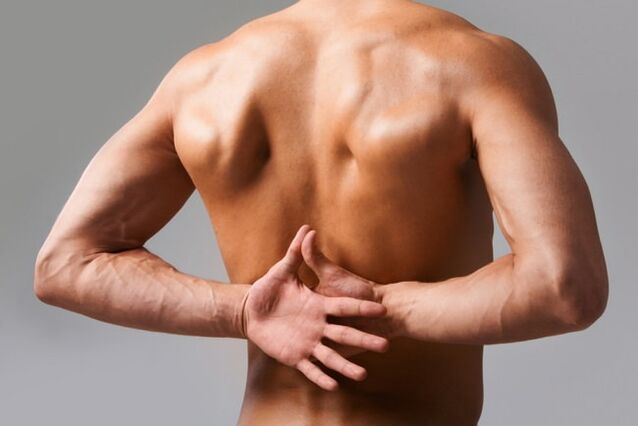
Because this anatomical part bears the greatest load, its structure is very strong and reliable. The lumbar spine is composed of five vertebrae that connect the thoracic cavity and the sacrum. Between them is the intervertebral disc, which gives the spine flexibility and flexibility. In turn, the intervertebral disc is composed of a jelly-like nucleus located within the hard fibrous ring. When osteochondrosis develops, the normal nutrition of the intervertebral discs is destroyed, as a result they become thinner, lose their elasticity, and the distance between them decreases. As a result, nerve roots are violated, causing severe pain and even disability.
Therefore, the reasons for the development of this pathology are:
- Spinal injury;
- Endocrine, digestive and cardiovascular diseases;
- Strenuous physical activity (weightlifting, hard running);
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Hormonal system failure;
- flatfoot;
- Abnormal intervertebral discs;
- elderly;
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
The risk factors for disease development are:
- Bent over and poor posture;
- Wrong lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet, obesity;
- Being in the wrong posture for a long time;
- genetic factors;
- pressure;
- Low temperature.
The main symptom of the disease is low back pain. It can be felt immediately or after strenuous exercise.
Other symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- Pain radiates to the lower back;
- Pain worsens after lifting weights, sneezing, coughing, or moving the body;
- Stiff body after being in one position for a long time;
- Continuous spasms of back muscles;
- Sudden pain after hypothermia (lower back pain);
- Violation of the sensitivity of the hips, thighs, calves and feet;
- Paralysis of the legs;
- Cold feet
- Foot artery spasm;
- Excessive sweating;
- The skin on the painful area is dry and peeling.
Any awkward movement can exacerbate osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, for example, when moving or turning the body to one side. In this case, the pain will not only appear in the lower back, but also in the legs. Waist cramps also have strong cramps, because in this way the body relieves the load on this part of the body. During the deterioration, a person finds a comfortable position for himself, where the pain subsides.
One of the complications of lumbar osteochondrosis is the dysfunction of the genitourinary system. Sometimes, increased urination and discomfort in the kidney area. Sciatic nerve inflammation and low back pain (lower back pain) may cause illness.
Stages of lumbar osteochondrosis
Unfortunately, osteochondrosis is an incurable disease, and the destruction of the intervertebral disc is irreversible. There are four levels of development of osteochondrosis:
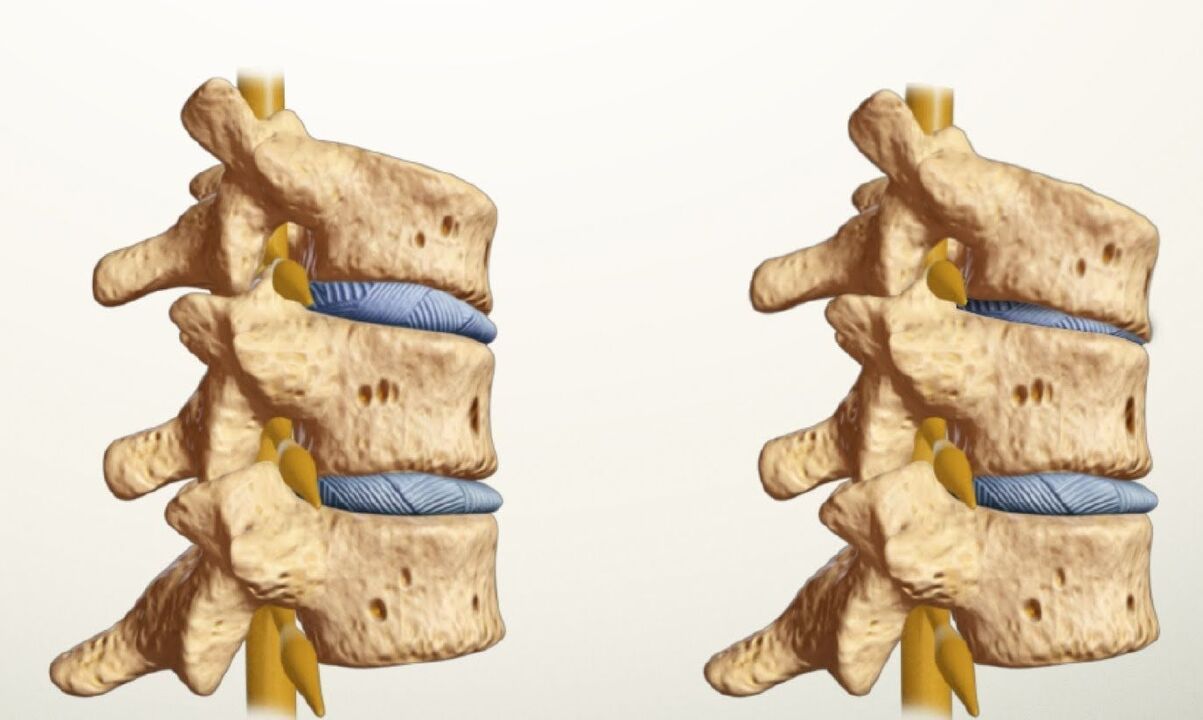
- In the first degree, the jelly-like nucleus in the intervertebral disc changes and moves.
- The second degree is the destruction of the annulus fibrosis of the intervertebral disc;
- The third degree, where the annulus fibrosus ruptures and the jelly-like nucleus leaves it, which leads to the formation of a herniated disc.
- The fourth degree is the developmental period of the degenerative process of the vertebrae in which the intervertebral joints and ligaments are involved. Arthropathy of the intervertebral joints (spondyloarthropathy) occurs.
First level
It is characterized by pain caused by stimulation of nerve endings located in the annulus fibrosus and longitudinal ligaments. The patient feels pain and discomfort in the affected part of the intervertebral disc. The pain can be severe, acute or dull, permanent and confined to the lumbosacral segment. Many times it will spread to the legs, and sometimes it will only be felt on the legs.
Stimulation of nerve endings leads to the development of reflex syndrome. For this reason, a person does not always feel pain in the problem area, but far beyond it. There is also the infringement of the internal organs of the robot, the occurrence of reflex muscle spasms; circulatory disturbances in the limbs and ligaments. Violation of blood circulation and nutrition of tendons and ligaments, resulting in pain and induration of bone attachment sites.
Second degree
At this stage, there is characteristic instability and increased mobility of the vertebrae, leading to continuous lubrication of the muscles. At the same time, it is difficult for a person to stand, and he will feel discomfort and pain in the waist. Sometimes the waist is "pain" and the patient does not understand why.
Three degrees
It is characterized by prolapse of intervertebral disc fragments, manifested as nerve root compression. During this period, there is a sensitive invasion of the innervated area of the compressed nerve. In addition, there are unpleasant sensations such as tingling, burning, numbness, and complete loss of sensitivity. Accompanied by impaired motor function, it sometimes leads to paralysis. In the affected area, muscle atrophy, thinning and reduction are observed. The areas where the above changes are observed eloquently indicate the location of spinal lesions. A characteristic manifestation of the third degree is the appearance of Lasseger symptoms. Manifestations: When lying on your back, straight legs up, severe pain in the waist, spreading along the back of the raised leg. When the legs were bent to the knees, the pain subsided immediately.

When fragments of the intervertebral disc fall into the lumen of the spinal canal, it can cause damage to the spinal cord. Another syndrome, the so-called ponytail, is manifested by impaired sensitivity and motor function of the legs, pelvic organs, and bladder.
Fourth degree
This period is characterized by the disappearance of pain and the recovery of the musculoskeletal system. However, at the same time, motor functions are also restricted. With the development of intervertebral disc fibrosis, the spine becomes lignified, and all its elements are replaced by dense scar tissue. At the same time, the intervertebral ligaments and joints are involved in the inflammatory process, and varying degrees of lesions are also observed, which are manifested as symptom polymorphisms.
How to treat lumbar osteochondrosis
The treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is a very long and lasting process. Most importantly, the successful treatment of the disease depends largely on the person himself. After all, he will have to completely change his lifestyle, get rid of many daily habits, and work hard for his health for the rest of his life.
In the opposite case, even successful medical treatment cannot completely eliminate the deformity of the spine. In addition, after a temporary improvement, the symptoms will return to a new intensity, and treatment must be restarted. Although sometimes, even if the physical exercise regime is followed, the onset of osteochondrosis will occur.
Therefore, the treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out in three ways:
- Conservative drug treatment;
- Non-drug
- Operation.
Conservative medication
Since osteochondrosis of the spine cannot be completely cured and is an irreversible process, the goal of conservative treatment is to eliminate symptoms and prevent further development of the disease. Before starting medication, it is necessary to minimize physical activity. If the condition worsens, it is recommended to stay in bed. This is sometimes more effective than drugs.
To relieve symptoms of inflammation, use:
- NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug). This group of drugs effectively eliminated the pain and inflammation of the vertebrae. The medicine can be a pill or an injection.
- Glucocorticoids. These drugs are classified as steroid hormones. Glucocorticoid injections are injected directly into the joint cavity. There is no doubt that they are supplemented with B vitamins (B1, B6, B12).
- sedative. They are necessary to eliminate reflexes and related psychogenic disorders.
- Anticonvulsants. Eliminate involuntary contraction of skeletal muscles.
- Antidepressants. This group of drugs affects the level of neurotransmitter, makes the patient's mood improved, and the depression, anxiety and emotional stress disappear.
- Diuretics. They are necessary for signs of nerve root syndrome.
- Anticholinesterase drugs. This group of drugs inhibits the activity of cholinesterase, so the conduction of nerve impulses increases.
- Cartilage protective agent. It is necessary to prevent deformation of the intervertebral discs and joints.
In acute attacks, novocaine blockers (introduction of anesthetic drugs directly into the affected area) are prescribed.
The symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis in women are different from those in men. In women, the menstrual cycle may be disturbed, and gynecological diseases may occur: inflammation of the ovaries and uterus (endometritis). Reproductive disorders can also occur. In this case, you need the help of a qualified gynecologist.
How to treat lumbar osteochondrosis at home
The main principle of family therapy is to eliminate the symptoms that prevent people from leading a quality lifestyle.
Use the following treatments at home:
- diet. In many cases, the cause of osteochondrosis is the accumulation of cholesterol and the loss of blood vessel elasticity. In order to remedy this situation, it is necessary to adhere to a low-fat diet. Also exclude high cholesterol foods from the diet: eggs, pork, soup, chicken skin. Eliminate alcohol and nicotine completely, reduce the intake of coffee and strong tea. They can cause vasospasm.
- Restore blood supply to the waist. To do this, you can use ointment rubs and compresses, as well as physical therapy exercises that can be performed at home.
- Orthopedic sleep aid. Since the spine is the central axis of the human body, it is under tremendous pressure during the day and requires proper rest. In this case, orthopedic mattresses and pillows work, they can provide the correct position for the spine during sleep.